Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue refers to advance payments a Company receives for products or services that are to be delivered or performed in the future.
It is also known as unearned revenue.
The company that receives the prepayment records the amount as Deferred Revenue on their balance sheet as a liability. Deferred revenue is a liability because it refers to revenue that has not been earned and represents products or services that are owed to a Customer. As the product or service is delivered over time, it is recognized as revenue on the income statement.
1. How to use Deferred Revenue
Internet and broadcasting service providers offer subscription plans on quarterly or yearly basis. They take complete payment in advance from the Customer for couple of months, but book income on monthly basis in their book of accounts. This is Deferred Revenue for the Supplier and Deferred Expense for the Customer. Following is how they should configure Deferred Revenue accounting in ERPNext to automate the process.
1.1 Item
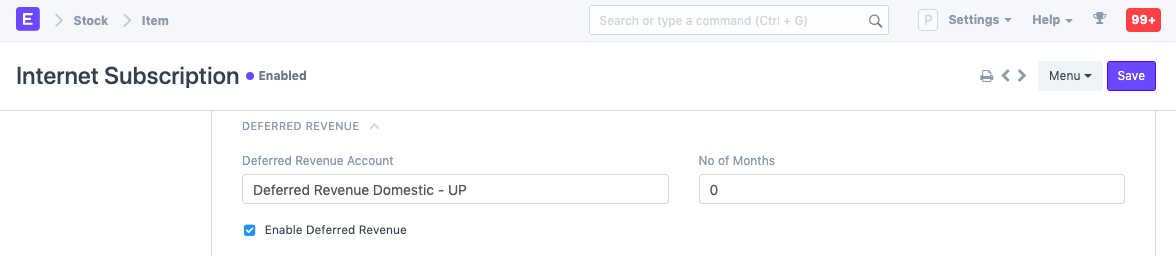
In the Item master created for the subscription plan, under Deferred Revenue section, check field Enable Deferred Revenue. You can also select a Deferred Revenue account for this particular item and number of months.
1.2 Sales Invoice
On creation of Sales Invoice for the Deferred Revenue Item, instead of posting in the Income Account, Deferred Revenue account is Credited by the sale amount. If you had set the account and period in Item, then the account and service start, end dates will be fetched automatically.
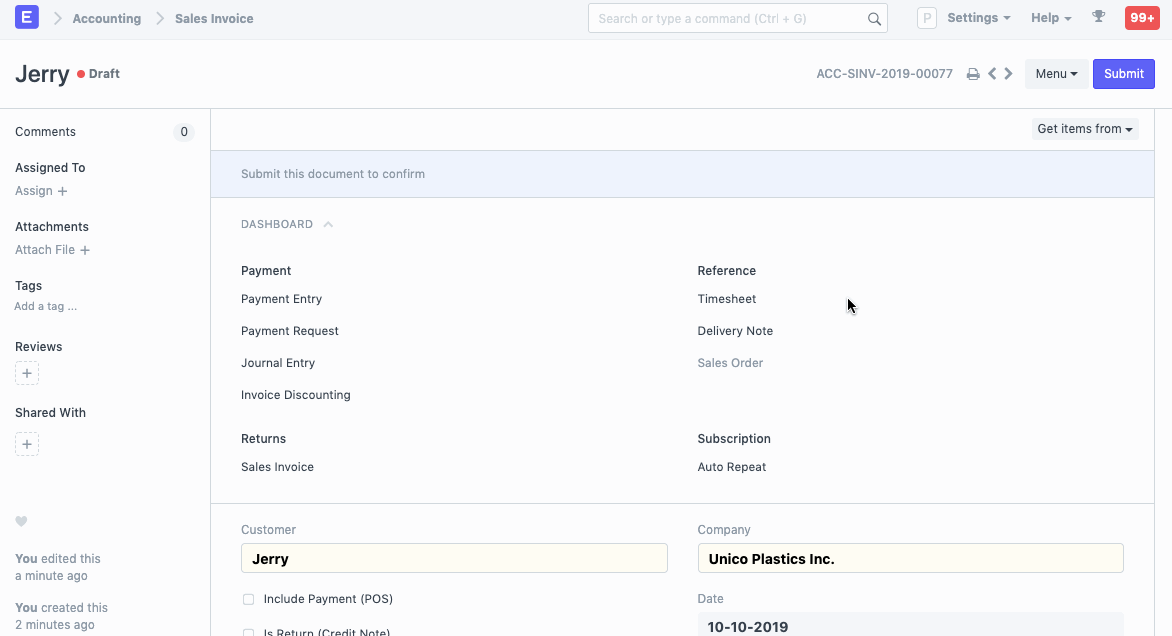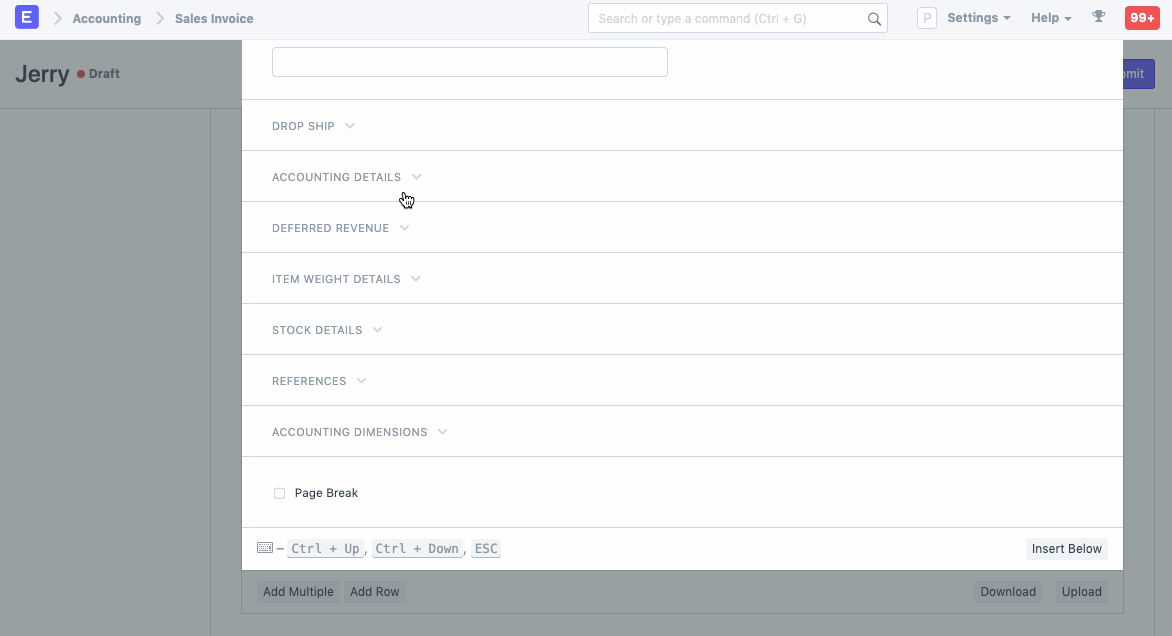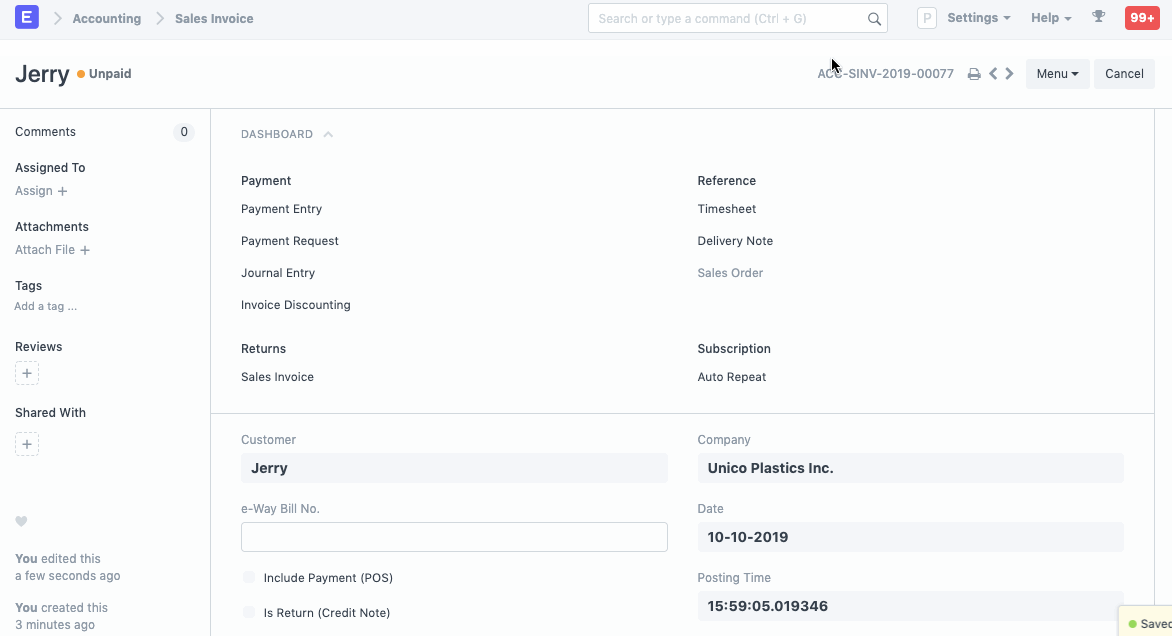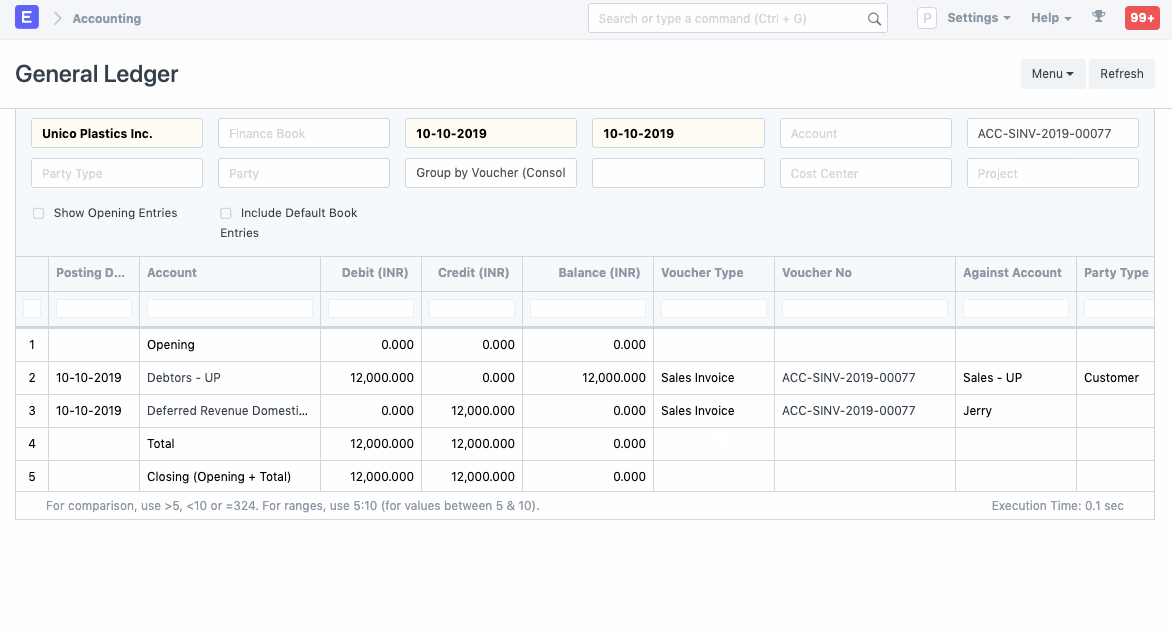
1.3 Journal Entry
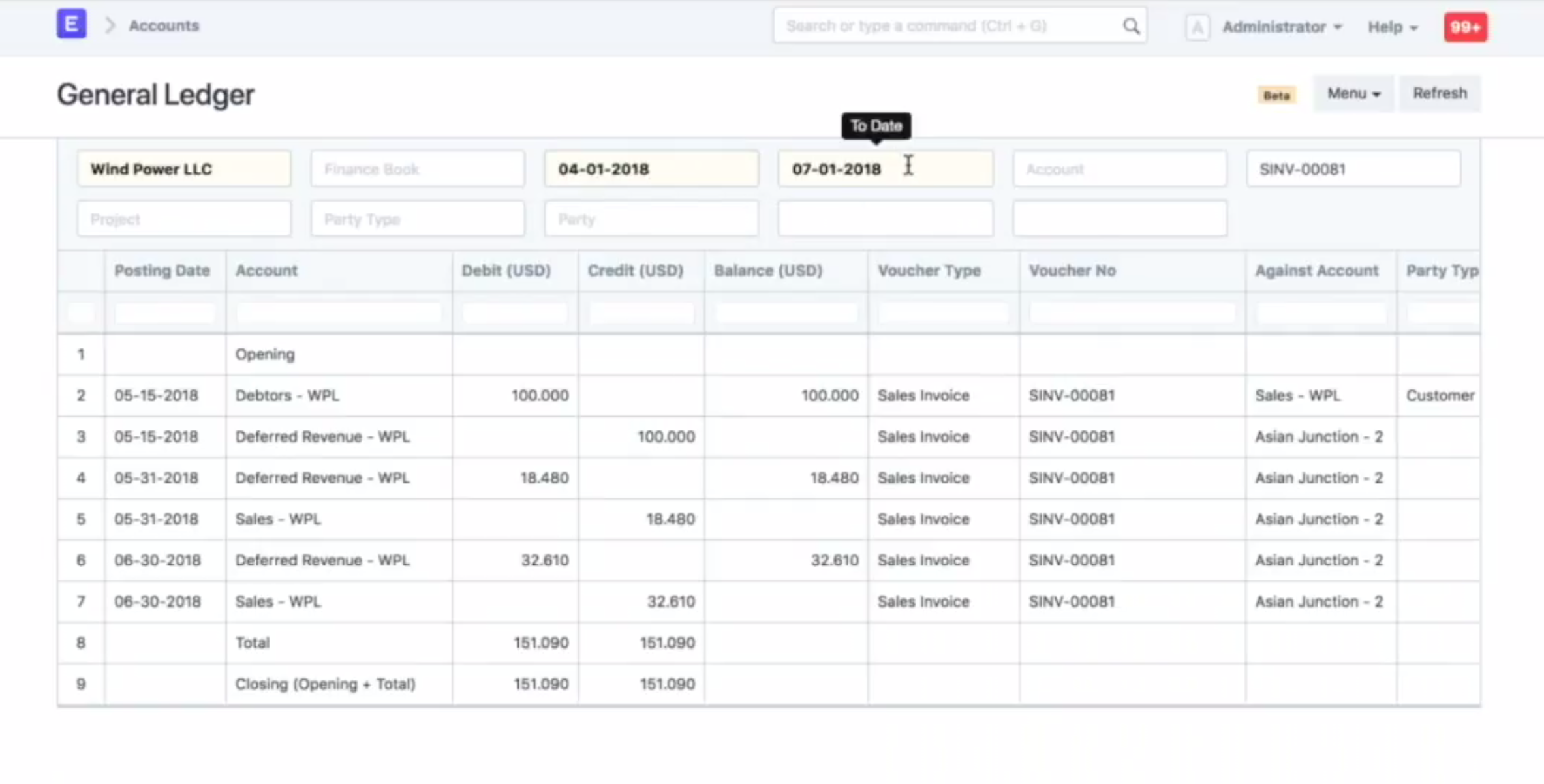
Based on the From Date and To Date set in the Sales Invoice Item table, Journal Entries are created automatically at the end of each month. It debits the value from Deferred Revenue account and credits Income Account selected for an Item in the Sales Invoice.
Following is an example of Income for the Deferred Revenue Item booked via multiple Journal Entries.