Perpetual Inventory
As per the perpetual inventory system, accounting entry is done for every stock transaction. Otherwise, it's done in larger intervals for example monthly or quarterly. Each warehouse is linked with a corresponding account head.
On receipt of items in a particular warehouse, the balance in the Warehouse Account will increase. Similarly, when items are delivered from the Warehouse, an expense will be booked, and the balance in the Warehouse Account will reduce.
1. How to activate perpetual inventory
Activate Perpetual Inventory:
Home > Accounting > Company > Enable Perpetual Inventory
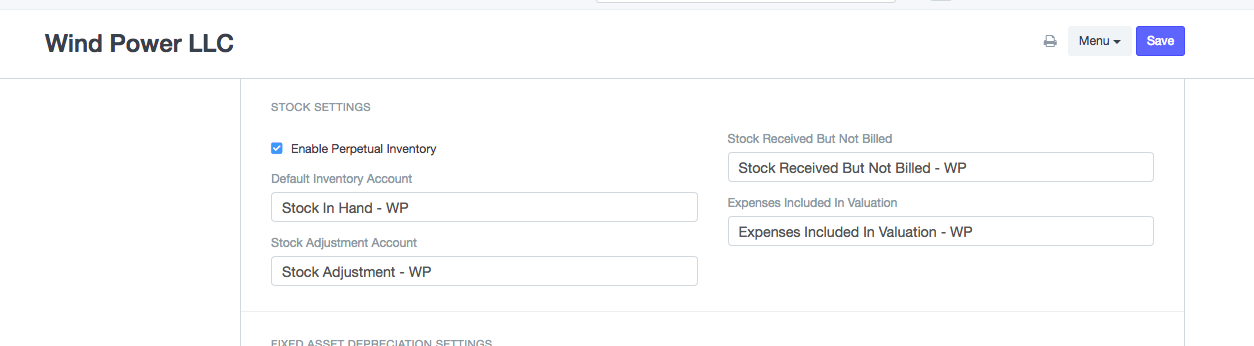 Note that if you disable perpetual inventory, users will have to manage the account entries manually.
Note that if you disable perpetual inventory, users will have to manage the account entries manually.Set up the following default accounts for each Company if not set. These accounts are created automatically in the new ERPNext accounts.
- Default Inventory Account (Asset)
- Stock Received But Not Billed (Liability)
- Stock Adjustment Account (Expense)
- Expenses Included In Valuation (Expense)
- Cost Center
If the user wants to set an individual account for each warehouse, create account head for each account. Go to:
Accounts > Chart of Accounts > Company > Application of Funds (Assets) > Current Asset > Stock Assets > Create a new account with same name as Warehouse
Now, go to a warehouse and link this account to the warehouse. This helps in filtering and viewing statements warehouse-wise.
For stock transactions, general ledger entries made against the Account Head set on the warehouse, if the user had not set the account for the warehouse then the system gets the account head from the parent warehouse. If Account was not set for parent warehouse then the system gets the account(Default Inventory Account) from the company master.
2. Example
Consider the following Chart of Accounts and Warehouse setup for your company:
Chart of Accounts:
- Assets (Dr)
- Current Assets
- Accounts Receivable
- Debtors
- Stock Assets
- Stores
- Finished Goods
- Work In Progress
- Tax Assets
- VAT
- Accounts Receivable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities (Cr)
- Current Liabilities
- Accounts Payable
- Creditors
- Stock Liabilities
- Stock Received But Not Billed
- Tax Liabilities
- Service Tax
- Accounts Payable
- Current Liabilities
- Income (Cr)
- Direct Income
- Sales Account
- Direct Income
- Expenses (Dr)
- Direct Expenses
- Stock Expenses
- Cost of Goods Sold
- Expenses Included In Valuation
- Stock Adjustment
- Stock Expenses
- Indirect Expenses
- Shipping Charges
- Customs Duty
- Direct Expenses
2.1 Warehouse - Account Configuration
- Stores
- Work In Progress
- Finished Goods
2.2 Purchase Receipt
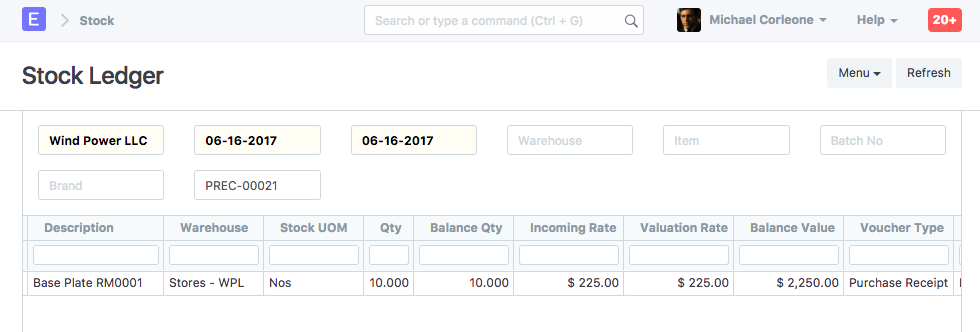
Suppose you have purchased 10 nos of item "RM0001" at $200 and 5 nos of item "Base Plate" at $100 from supplier "Arcu Vel Quam Fabricators". Following are the details of Purchase Receipt:
Supplier: Arcu Vel Quam Fabricators
Items:
| Item | Warehouse | Qty | Rate | Amount | Valuation Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM0001 | Stores | 10 | 200 | 2000 | 2250 |
Taxes:
| Account | Amount | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Shipping Charges | 100 | Total and Valuation |
| VAT (10%) | 200 | Total |
| Customs Duty | 150 | Valuation |
Stock Ledger
General Ledger
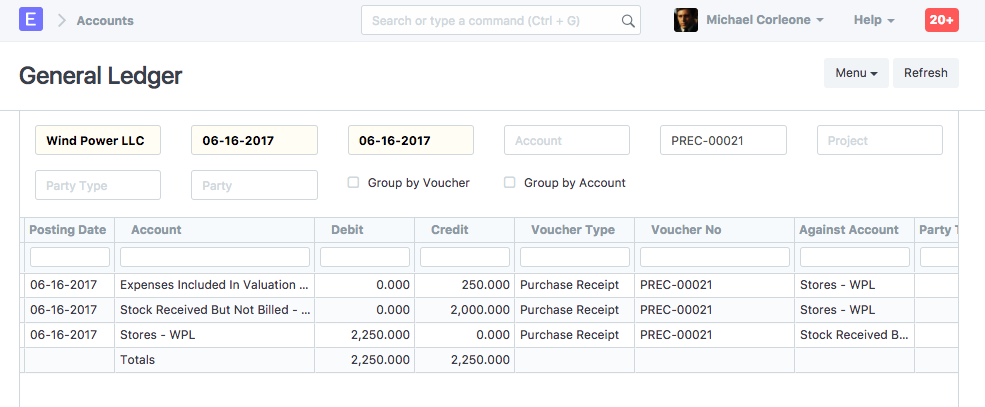
As stock balance increases through Purchase Receipt, "Store" accounts are debited and a temporary account "Stock Receipt But Not Billed" account is credited, to maintain double-entry accounting system. At the same time, the negative expense is booked in account head having category as "Valuation" or "Total and Valuation" in taxes and charges table for the amount added for valuation purpose, to avoid double expense booking.
2.3 Purchase Invoice
On receiving Bill from supplier, for the above Purchase Receipt, you will make Purchase Invoice for the same. The general ledger entries are as follows:
General Ledger
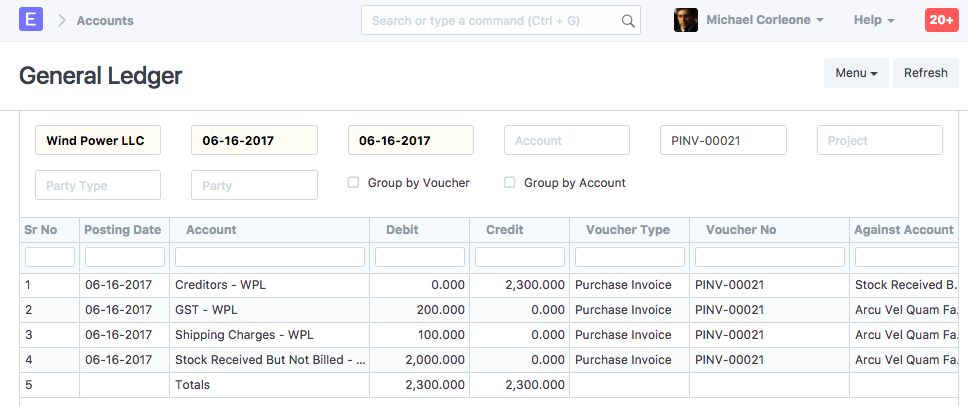
Here "Stock Received But Not Billed" account is debited and nullified the effect of Purchase Receipt.
2.4 Delivery Note
Let's say, you have an order from "Utah Automation Services" to deliver 5 nos of item "RM0001" at $300. Following are the details of Delivery Note:
Customer: Utah Automation Services
Items:
| Item | Warehouse | Qty | Rate | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM0001 | Stores | 5 | 300 | 1500 |
Taxes:
| Account | Amount |
|---|---|
| Service Tax | 150 |
| VAT | 100 |
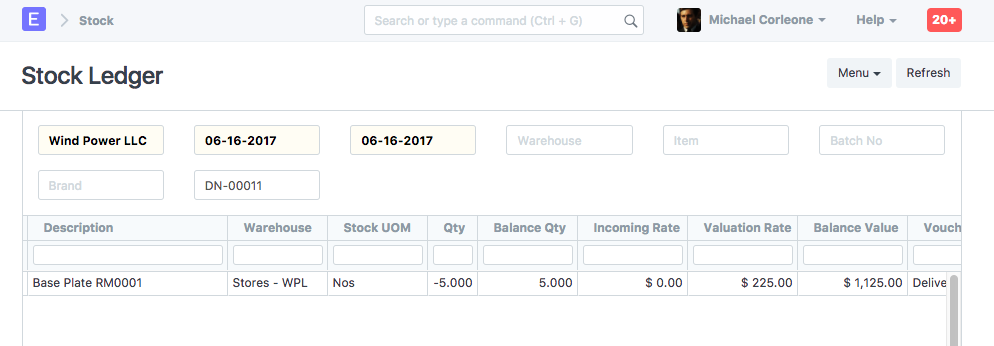
Stock Ledger
General Ledger
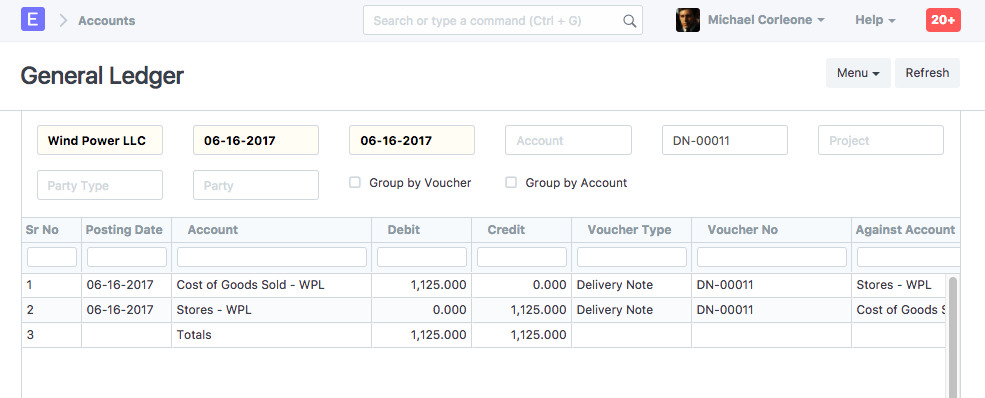
As an item is delivered from "Stores" warehouse, "Stores" account is credited and an equal amount is debited to the expense account "Cost of Goods Sold". The debit/credit amount is equal to the total valuation amount (buying cost) of the selling items. And the valuation amount is calculated based on your preferred valuation method (FIFO / Moving Average) or actual cost of serialized items.
In this example, we have considered the valuation method as FIFO.
Valuation Rate = Purchase Rate + Charges Included in Valuation
= 200 + (250 / 10)
= 225
Total Valuation Amount = 220 * 5
= 1125
2.5 Sales Invoice with Update Stock
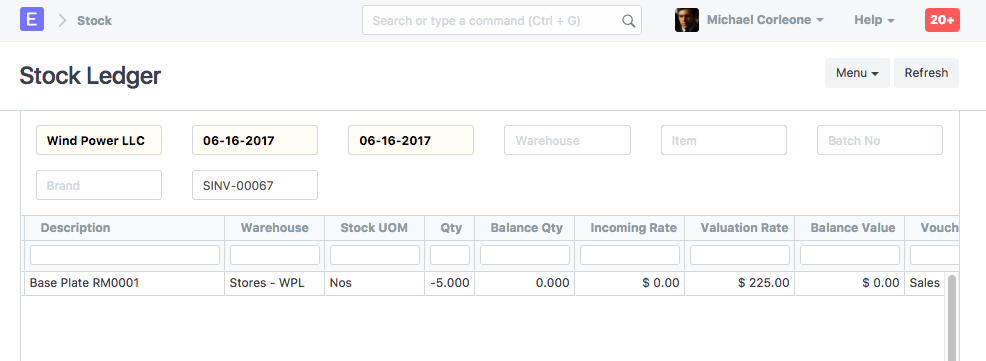
Let's say, you did not make Delivery Note against the above order and instead, you have made Sales Invoice directly, with "Update Stock" options. The details of the Sales Invoice are same as the above Delivery Note.
Stock Ledger
General Ledger
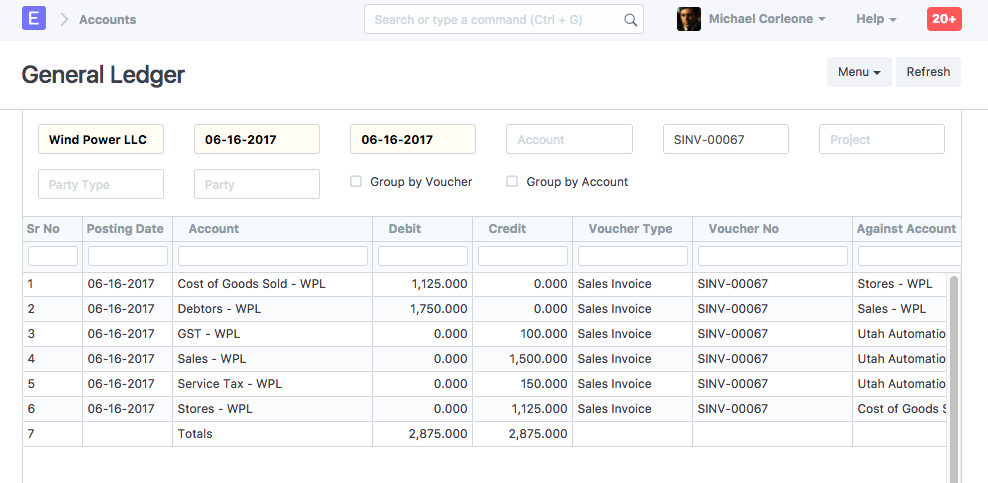
Here, apart from normal account entries for an invoice, "Stores" and "Cost of Goods Sold" accounts are also affected based on the valuation amount.
2.6 Stock Entry (Material Receipt)
Items:
| Item | Target Warehouse | Qty | Rate | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
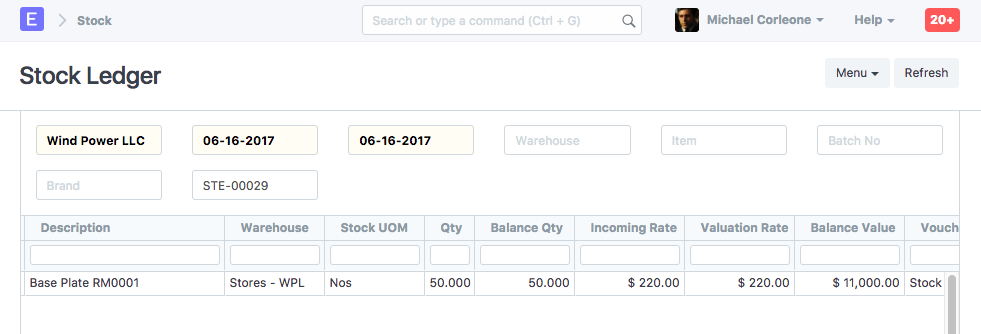
| RM0001 | Stores | 50 | 220 | 11000 |
Stock Ledger
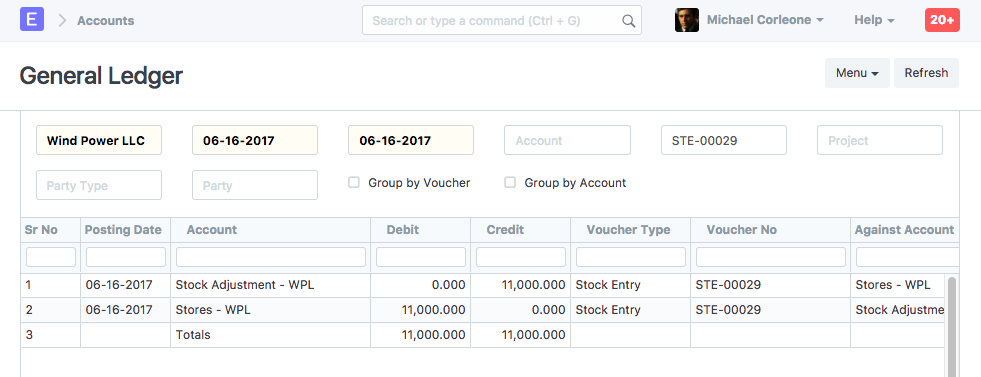
General Ledger
2.7 Stock Entry (Material Issue)
Items:
| Item | Source Warehouse | Qty | Rate | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM0001 | Stores | 10 | 220 | 2200 |
Stock Ledger
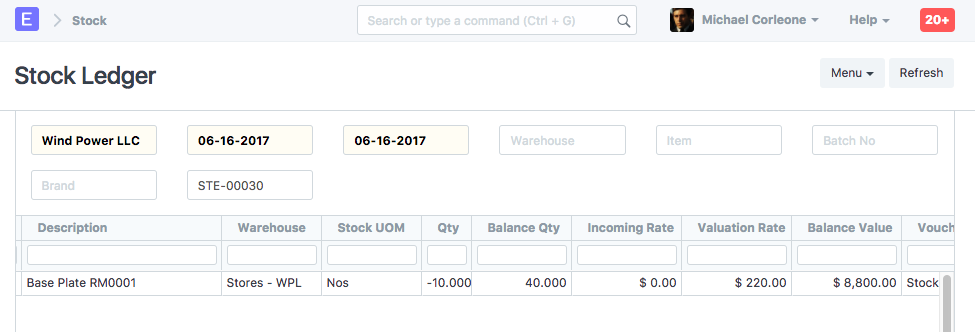
General Ledger
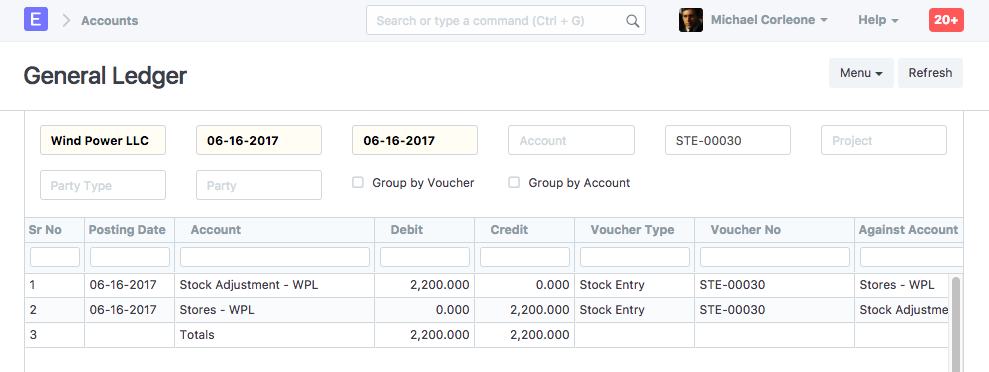
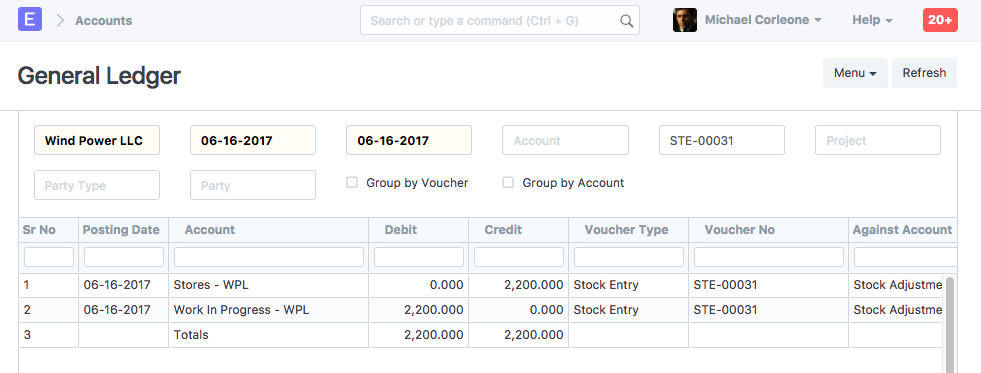
2.8 Stock Entry (Material Transfer)
Items:
| Item | Source Warehouse | Target Warehouse | Qty | Rate | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM0001 | Stores | Work In Progress | 10 | 220 | 2200 |
Stock Ledger
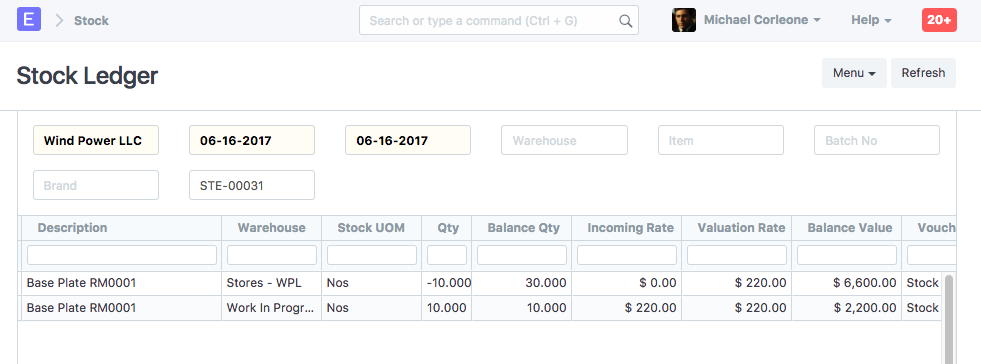
General Ledger