Tax Withholding Category
Tax Withholding Category is Tax Deducted at Source.
According to this, a person responsible for making payments is required to deduct tax at source at prescribed rates. Instead of receiving tax on your income from you at a later date, the govt wants the payers to deduct tax beforehand and deposit it with the government.
To access the Tax Withholding Category list, go to:
Home > Accounting > Taxes > Tax Withholding Category
1. Prerequisites
Before creating and using a Tax Withholding Category, it is advised to create the following first: 1. Supplier
2. How to create a Tax Withholding Category
In ERPNext, Tax Withholding Categories for most cases are available by default, however, you can create more if needed.
- Go to the Tax Withholding Category list and click on New.
- Enter a unique name, eg: Section 194C Individual.
- Enter a Category Name (Dividends, Professional Fees, etc,.).
- Enter a Tax Withholding Rate against a Fiscal Year.
- You can set the threshold for a single invoice or sum of all invoices.
- Select an account against your Company to which tax will be credited.
- Add more companies and accounts as needed.
Save.
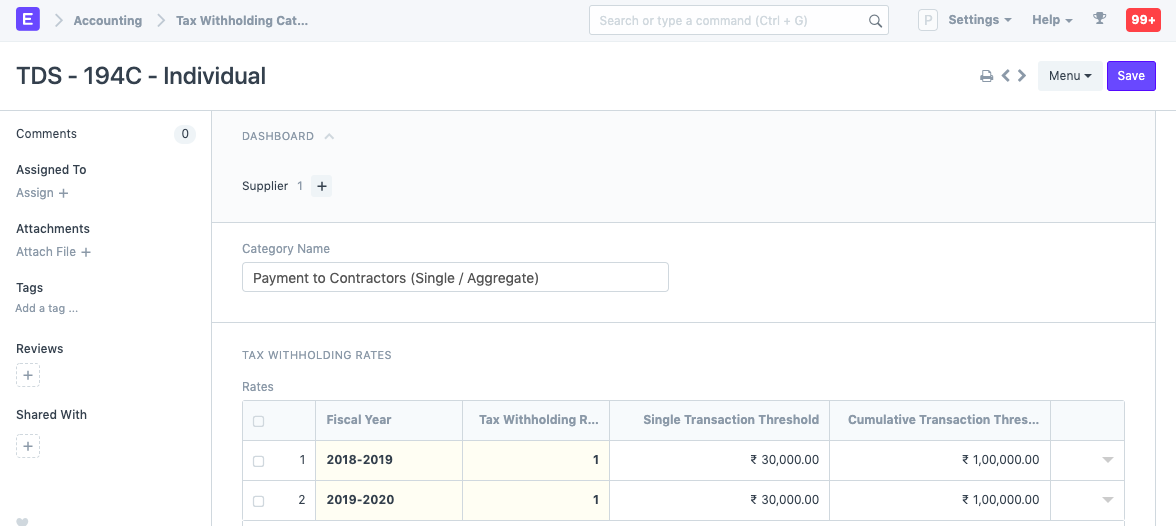
Under accounting details, the TDS account is added for each Company in the system.
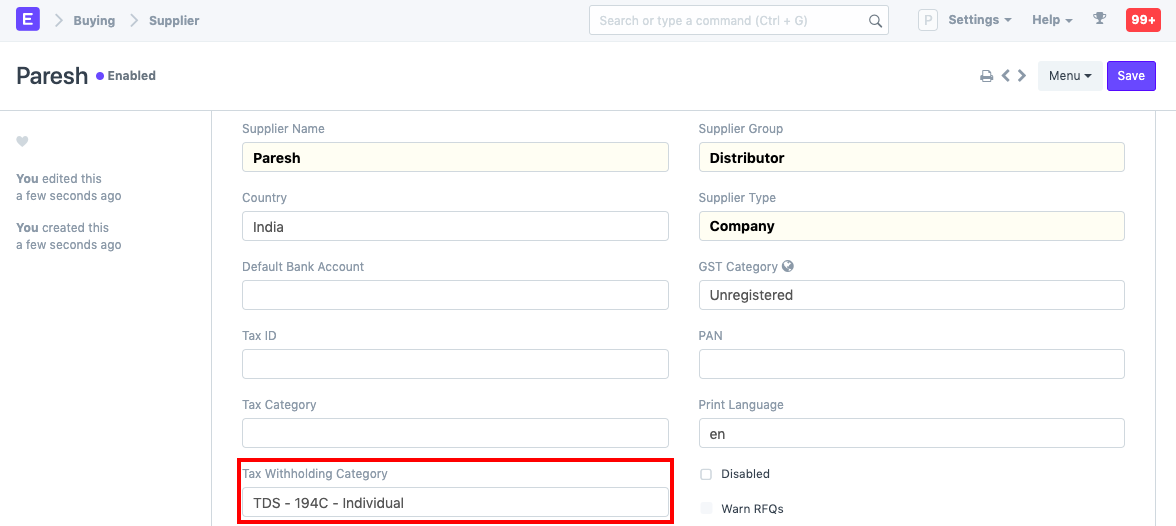
2.1 Assigning Tax Withholding to Supplier
After saving, it can be assigned to a Supplier:
2.2 How does the threshold work?
Consider a Supplier on whom a Tax Withholding Category is applied.
For example, let's say a rate of 5% will be applicable on invoice where Single threshold is 20,000 and the Cumulative threshold is 30,000. If an invoice is created with a grand total of 20,000 then the single threshold will be triggered and a 5% tax would be charged.
But if the invoice amount totaled up to be 15,000 then no tax will be charged as it didn't cross the threshold. If again another invoice is created against the same supplier with a total of 15,000 then although it didn't cross the Single threshold, charges will be deducted since the sum of the last invoice and this invoice adds up to be 30,000 which is equal to the specified Cumulative threshold.
3. Using Tax Withholding
3.1 Use in Purchase Invoice
In the following example, we have selected 'TDS - 194C - Individual' which has a single threshold of 30,000, cumulative threshold of 1,00,000 and rate of 1%.
If the Supplier has the tax withholding field set, then upon selecting that Supplier, a checkbox will become visible in the Purchase Invoice to select whether to apply tax or not.
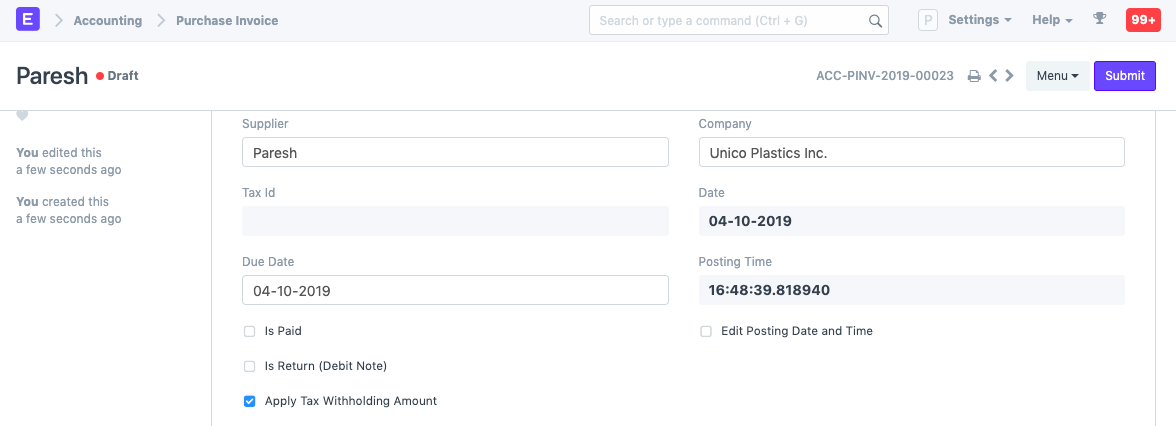
Let's create an invoice for 90,000. Saving the invoice automatically calculates tax and appends it in the taxes table.
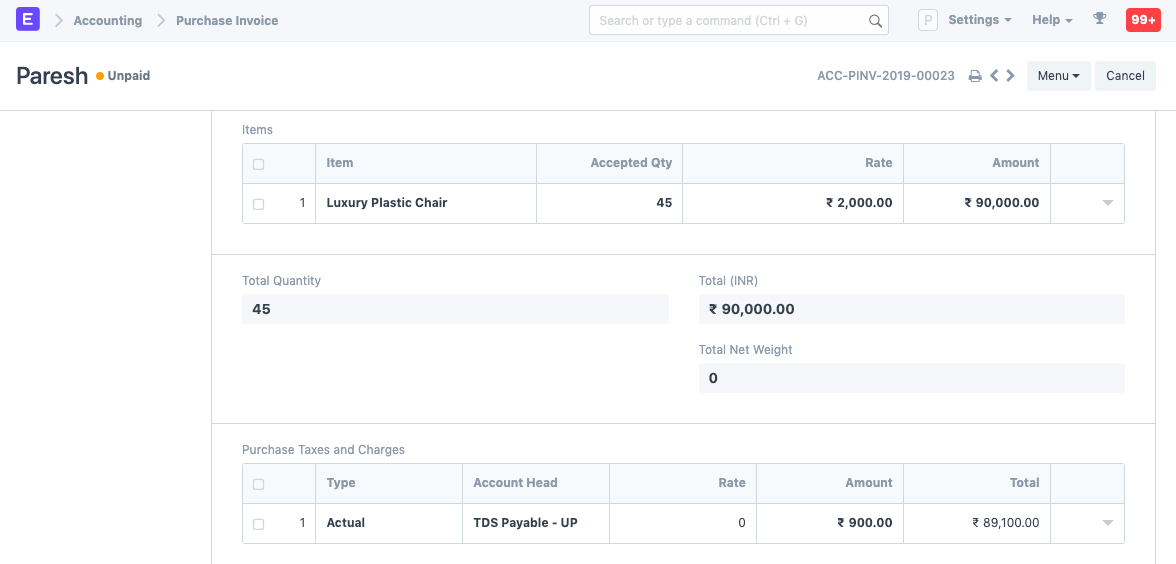
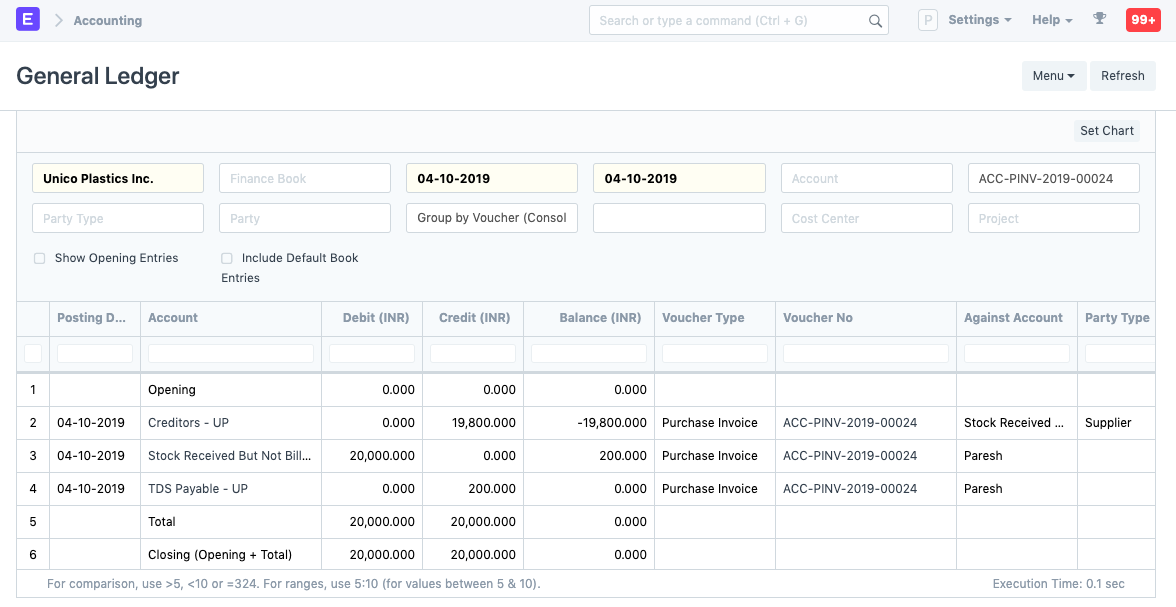
To see the effect of Cumulative threshold, let's create an invoice with of amount 20,000 and submit it.
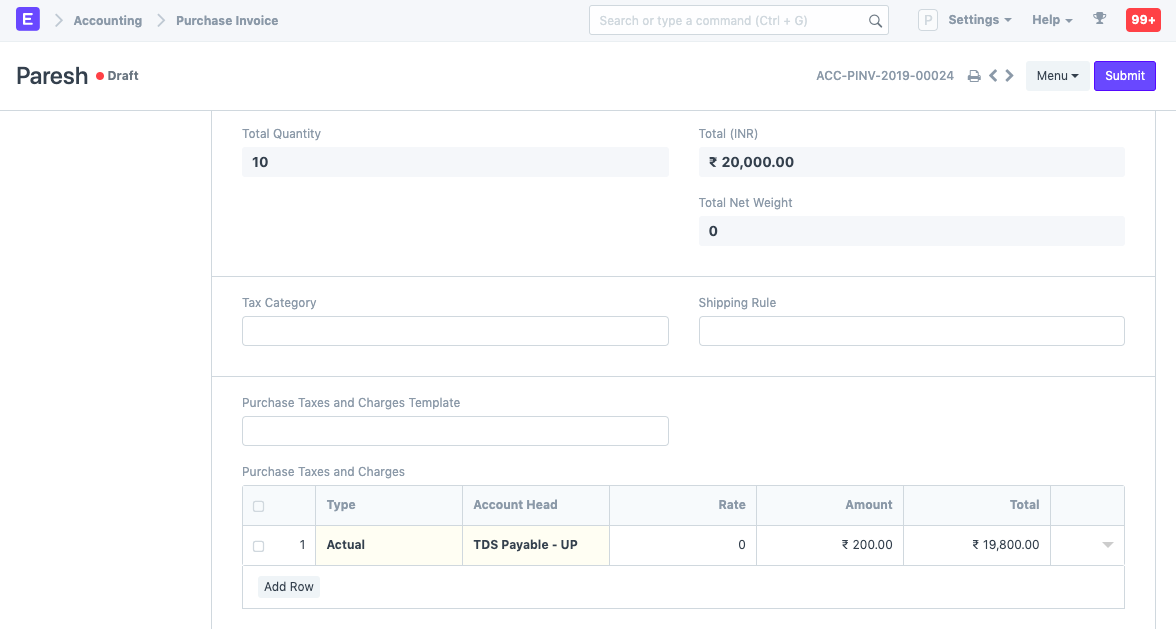
Although the invoice amount didn't cross the Single threshold (30,000), we see that tax has been charged. This is because the previous and the current invoice adds up to be 1,10,000 which exceeds the Cumulative threshold. Hence, tax based on the rate provided in the Tax Withholding Category is applied accordingly.
Note: On submitting the invoice, three GL Entries are created:
- First for debit from the expense head
- Second for credit in Creditors account
- Third for credit in the account selected in Tax Withholding Category.